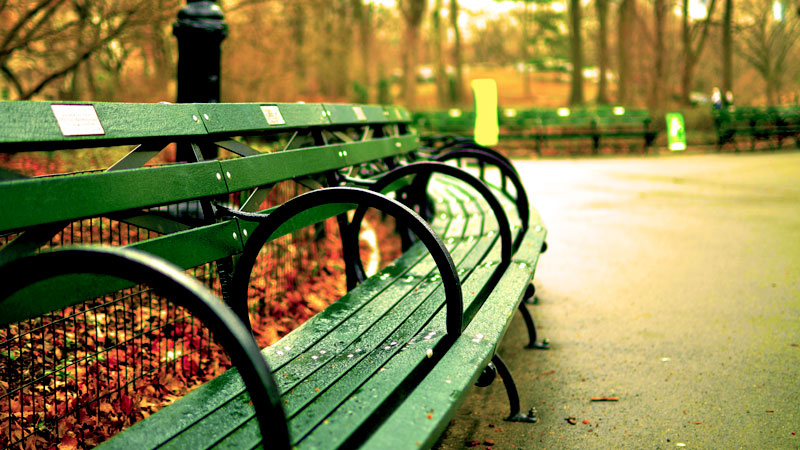
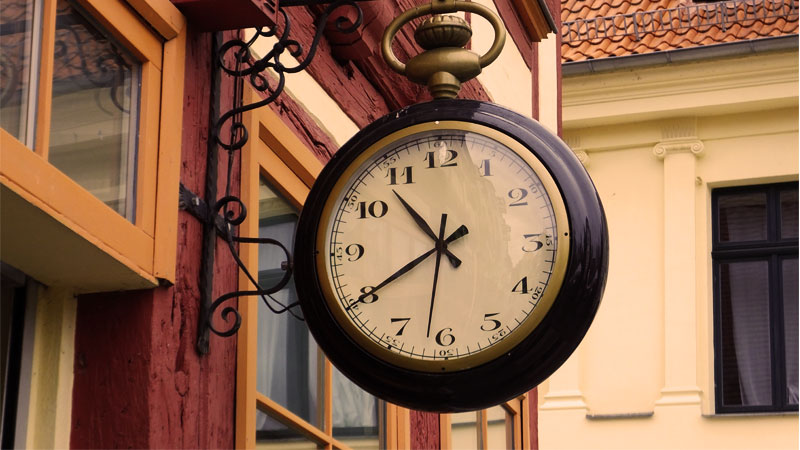
Scrabble game getting a bit of a makeover, at least in Europe
new york — Scrabble is getting a bit of a makeover, at least in Europe.
New version advertised as being more team-oriented and quicker to play
Mattel has unveiled a double-sided board that features both the classic word-building game and Scrabble Together, a new rendition designed to be accessible “for anyone who finds word games intimidating.”
This new version, which is now available across Europe, is advertised as being more team-oriented and quicker to play. The update marks the first significant change to Scrabble’s board in more than 75 years, Mattel said Tuesday.
“We want to ensure the game continues to be inclusive for all players,” Ray Adler, vice president and global head of games at Mattel said in a prepared statement, noting that consumers will still be able to choose between the classic game and new version.
Seeking to expand their reach, toy companies have rolled out alternative or simplified ways to play board games for years, ranging from “junior” editions made for younger children to multiple sets of instructions that players can opt into for increasing difficulty.
Scrabble Together is marketed toward players of all ages. Jim Silver, a toy-industry expert and CEO of review site TTPM, said the double-sided board is a smart approach because it allows players to switch from one mode to another as they wish.
Mattel’s announcement was also accompanied by a survey that offered a glimpse into some of the ways British consumers have previously tackled classic Scrabble. London-based market researcher Opinion Matters found that 75% of U.K. adults aged 25 to 34 have searched a word when playing the board-and-tile game to check if it’s real. And almost half (49%) reported trying to make up a new word in hopes of winning.
Whether the new version will expand beyond Europe one day remains to be seen.
While Mattel, which is based in El Segundo, California, owns the rights to Scrabble around much of the world, Hasbro licenses the game in the U.S., for example.
“Mattel and Hasbro have worked separately to develop different versions of Scrabble every year,” Silver said. As a result, some versions are only available in certain countries, creating an “interesting dynamic” for avid fans of the game, he added.
A spokesperson for Hasbro, based in Pawtucket, Rhode Island, confirmed to The Associated Press via email Tuesday that the company currently has no plans for a U.S. update — but added that the brand “love[s] the idea of different ways to play Scrabble and continue[s] to attract new players to the game around the world.”
Scrabble’s origins date back to 1931, when American architect Alfred Mosher Butts invented the game’s forerunner. Scrabble’s original name was “Lexiko,” according to a Mattel factsheet, and before officially getting the Scrabble title and trademark in 1948, Butts’ creation was also called “Criss-Crosswords,” “It” and “Alph.”
Today, Scrabble is produced in 28 different languages. More than 165 million games have been sold in 120 countries around the world since 1948, according to Mattel, with an average of 1.5 million games sold globally each year.
Beyond the decades-old Scrabble fanbase, other word games have skyrocketed in popularity in recent years, including Bananagrams and online guessing game Wordle.
…
Ukrainians honored for saving animals during war
Animal rights groups and political leaders are honoring volunteers and activists who are saving animals affected by the war in Ukraine. Among those being recognized is Maria Vronska, who runs a Kyiv-area shelter that cares for more than 700 dogs and cats. Anna Kosstutschenko reports. Camera: Pavel Suhodolskiy.
…
US: China strengthens Russian war machine with surging equipment sales
WASHINGTON — China has surged sales to Russia of machine tools, microelectronics and other technology that Moscow in turn is using to produce missiles, tanks, aircraft and other weaponry for use in its war against Ukraine, according to a U.S. assessment.
Two senior Biden administration officials, who discussed the sensitive findings Friday on the condition of anonymity, said that in 2023 about 90% of Russia’s microelectronics came from China. Russia has used those to make missiles, tanks and aircraft. Nearly 70% of Russia’s approximately $900 million in machine tool imports in the last quarter of 2023 came from China.
Chinese and Russian entities have also been working to jointly produce unmanned aerial vehicles inside Russia, and Chinese companies are likely providing Russia with the nitrocellulose used in the manufacture of ammunition, the officials said. China-based companies Wuhan Global Sensor Technology Company, Wuhan Tongsheng Technology Company and Hikvision are providing optical components for use in Russian tanks and armored vehicles.
The officials said that Russia has received military optics for use in tanks and armored vehicles manufactured by Chinese firms iRay Technology and North China Research Institute of Electro-Optics, and that China has been providing Russia with UAV engines and turbojet engines for cruise missiles.
Russia’s semiconductor imports from China jumped from $200 million in 2021 to over $500 million in 2022, according to Russian customs data analyzed by the Free Russia Foundation, a group that advocates for civil society development.
Beijing is also working with Russia to improve its satellite and other space-based capabilities for use in Ukraine, a development the officials say could in the longer term increase the threat Russia poses across Europe. The officials, citing downgraded intelligence findings, said the U.S. has also determined that China is providing imagery to Russia for its war on Ukraine.
The officials discussed the findings as U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken is expected to travel to China this month for talks. Blinken is scheduled to travel next week to the Group of 7 foreign ministers meeting in Capri, Italy, where he’s expected to raise concerns about China’s growing indirect support for Russia as Moscow revamps its military and looks to consolidate recent gains in Ukraine.
U.S. President Joe Biden has previously raised concerns directly with Chinese President Xi Jinping about Beijing indirectly supporting Russia’s war effort.
While China has not provided direct lethal military support for Russia, it has backed it diplomatically in blaming the West for provoking Russian President Vladimir Putin’s decision to launch the war and refrained from calling it an invasion in deference to the Kremlin.
China has repeatedly said it isn’t providing Russia with arms or military assistance, although it has maintained robust economic connections with Moscow, alongside India and other countries, amid sanctions from Washington and its allies.
“The normal trade between China and Russia should not be interfered or restricted,” said Liu Pengyu, spokesperson of the Chinese Embassy in Washington. “We urge the U.S. side to refrain from disparaging and scapegoating the normal relationship between China and Russia.”
Xi met in Beijing on Tuesday with Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov, who heaped praise on Xi’s leadership.
Russia’s growing economic and diplomatic isolation has made it increasingly reliant on China, its former rival for leadership of the Communist bloc during the Cold War.
U.S. Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen, who returned to Washington this week from a visit to Beijing, said she warned Chinese officials that the Biden administration was prepared to sanction Chinese banks, companies and Beijing’s leadership if they assist Russia’s armed forces with its ongoing invasion of Ukraine.
Biden issued an executive order in December giving Yellen the authority to sanction financial institutions that aided Russia’s military-industrial complex.
“We continue to be concerned about the role that any firms, including those in the PRC, are playing in Russia’s military procurement,” Yellen told reporters, using the initials for the People’s Republic of China. “I stressed that companies, including those in the PRC, must not provide material support for Russia’s war and that they will face significant consequences if they do. And I reinforced that any banks that facilitate significant transactions that channel military or dual-use goods to Russia’s defense industrial base expose themselves to the risk of U.S. sanctions.”
The United States has frequently downgraded and unveiled intelligence findings about Russia’s plans and operations over the course of the war with Ukraine, which has been fought for more than two years.
Such efforts have been focused on highlighting plans for Russian misinformation operations or to throw attention on Moscow’s difficulties in prosecuting its war against Ukraine as well as its coordination with Iran and North Korea to supply it with badly needed weaponry. Blinken last year spotlighted intelligence that showed China was considering providing arms and ammunition to Russia.
The White House believes that the public airing of the intelligence findings has led China, at least for now, to hold off on directly arming Russia. China’s economy has also been slow to emerge from the COVID-19 pandemic. Chinese officials could be sensitive to reaction from European capitals, which have maintained closer ties to Beijing even as the U.S.-China relationship has become more complicated.
…
Germany detains Iraqi couple suspected of genocide against Yazidis
WASHINGTON — German officials are interrogating an Iraqi couple who are suspected of committing crimes that may amount to genocide while they were associated with the Islamic State group in Iraq and Syria between October 2015 and December 2017.
The German federal public prosecutor general released a statement Wednesday saying “Twana H.S. and Asia R.A. are strongly suspected of genocide according to the German Code of Crime” against Yazidis, a religious minority that was targeted by the Islamic State militant group in 2014.
The two, who were not further identified, were arrested this week in Regensburg and Roth County, Germany.
In March, the investigating judge at the Federal Court of Justice issued arrest warrants for them and ordered that “they be placed in pretrial detention.” It has been reported that the couple are originally from the Iraqi Kurdistan region.
Prosecutors said the couple “held a then-5-year-old Yazidi girl; they enslaved a then-12-year-old Yazidi girl as well. Twana repeatedly raped both children. To this end, Asia prepared the room and put makeup on one of the girls.”
Islamic State attacked Yazidis in the Sinjar region in Iraq on August 3, 2014, with a systematic plan to commit genocide against the Yazidis because it considered them to be religious infidels.
According to Yazidi sources, the extremist group killed thousands of people and enslaved approximately 6,500 people, mainly women and children. Mirza Dinnayi, a founder of the nongovernmental organization House of Coexistence in Sinjar, told VOA there are still about 2,650 women and children missing.
IS attacks in Sinjar displaced more than 375,000 people from their homes. After more than nine years, most of them still live in a dozen camps in Iraqi Kurdistan and northeastern Syria.
More than 80 mass graves of Yazidis from Sinjar were found in the region. Half of them have not been exhumed. So far, the remains of 200 of the victims have been identified using DNA technology.
The parliaments of several countries and international institutions, including the U.S., U.K., Belgium, Netherlands, Canada, Australia, Armenia and Germany, have labeled the atrocities as genocide.
It is not the first time a court in Germany will try IS members for genocide crimes against Yazidis. On November 30, 2021, a court in Frankfurt found 29-year-old Taha al-Jumailly, an Iraqi national, guilty “of involvement in the slaughter of more than 3,000 Yazidis and enslavement of 7,000 women and girls by IS jihadists in 2014-2015.” The court ruling included the murder of a 5-year-old girl the defendant had enslaved and chained to a window, leaving her to die in scorching heat.
Irfan Ortach, chairman of the Central Council of the Yazidis in Germany, said after the German parliament recognized the “massacre of Yazidis by jihadists from the Islamic State in Iraq as genocide” in January 2023, the perspective of courts in Germany changed on the role of women in the atrocities committed in Iraq and Syria.
Ortach told VOA that “prior to that there was an understanding in German courts that women had no role in the radical organization and its acts. But now they are equally subject of investigations and trials.”
The Regensburg case will likely be similar to the Frankfurt case in terms of the nature of crimes and the ages of the victims.
According to the German federal prosecutor’s office, before leaving Syria in November 2017, Twana H.S. and Asia R.A. handed the girls over to other IS members. Yazidi activists say both girls are now under German authorities’ protection.
This story originated in VOA’s Kurdish Service.
…
German chancellor heads to Beijing amid efforts to balance trade, geopolitical concerns
TAIPEI, TAIWAN — German Chancellor Olaf Scholz will kick off a three-day visit to China Saturday, aiming to double down on Germany’s deep economic ties with China amid rising trade tension between Beijing and the European Union.
Making his first trip to China since his government released its first China strategy in July, stressing the need to lower economic dependence on China, Scholz will be accompanied by executives from major German companies, such as Siemens, Volkswagen, and Bayer, and three Cabinet ministers.
Some analysts say bilateral economic relations will be the main focus of Scholz’s trip.
“He will try to focus on the positive things in the German-China relationship and try to foster more partnership and cooperation in critical areas relevant to key German industries,” Max Zenglein, chief economist at the Mercator Institute for China Studies in Berlin, told VOA in a video interview Wednesday.
The visit comes as some key German industries see falling revenues in China. According to automobile company data reported by Reuters Wednesday, several German premium carmakers have seen China sales fall significantly in the year’s first quarter, with Mercedes-Benz and Porsche showing double-digit percentage falls in their sales in China.
In addition, a recent report by the New York-based research firm Rhodium Group found that Germany’s automotive industry faces fierce Chinese competition, with German companies’ market share in China falling 4% since 2018.
“The losses have come mainly from volume producer Volkswagen, which sold fewer cars in China in 2023 than it did in 2013,” the report said, adding that the market share of Volkswagen’s Chinese venture fell to the lowest point in a decade even though the overall passenger vehicle market in China grew by 5.6%.
Instead of reevaluating their approach to the Chinese market, Rhodium Group found that some of these companies have reinvested the profits they made in China in the country “in a push to remain competitive.”
Zenglein said Scholz will likely focus on helping some German companies that rely heavily on China to maintain their economic interests in the country during his visit.
Scholz may feel the need to “signal to the corporate sector that he is willing to give the appropriate political flanking for their economic interests,” he told VOA.
Other experts say some German companies are struggling to adapt to changes taking place in the Chinese market because they have become too reliant on the benefits the market offers.
“At a time when the German economy is facing pressure from multiple fronts, including the country’s need to support Ukraine and the sluggish economic performance, the German government will try to maintain a close economic and trade relationship with China in the short term so German products can keep selling to the Chinese market,” said Zhang Junhua, a senior associate at the European Institute for Asian Studies in Brussels.
However, he said he thinks these efforts will contradict the German government’s call for companies to reduce economic dependence on China.
“Since Germany’s economic performance remains sluggish, the government has to give in to pressure from the business sector and make compromises on executing the China Strategy, which urges German companies to de-risk from China,” Zhang told VOA by phone.
German companies ‘swim against the international trend’
Meanwhile, the EU has launched a series of antisubsidies investigations against green energy products imported from China, including electric vehicles and wind turbines.
EU Commissioner Margrethe Vestager said the bloc needed a more systematic approach to handle the investigations. “We need to do it before it is too late, [and] we can’t afford to see what happened on solar panels happening again on electric vehicles, wind or essential chips,” she said Tuesday, referring to China’s dominance in the European solar panel market.
In response, the Chinese Commerce Ministry said Thursday that it resolutely opposed the EU investigations, calling them “a protectionist act that harms the level playing field in the name of fair competition.”
“China will closely monitor the European side’s subsequent movements and reserves the right to take all necessary measures,” the ministry said in a statement.
While Scholz’s chief economic adviser, Joerg Kukies, said Berlin supports the EU’s antisubsidy probe into Chinese electric vehicles at a think tank event in Berlin last September, Scholz told German business weekly Wirtschaftswoche in an interview the same month that he is “not convinced” about the need for the EU to impose tariffs on Chinese EVs.
“Our economic model should not be based or rely on protectionism – but on the attractiveness of our products,” Scholz said in the interview.
In Zenglein’s view, some German companies’ growing investment in China is “swimming against the international trend. “The trend is driven by capital-intensive sectors like automotive and chemical,” Zenglein said. According to the Rhodium Group report, major German carmakers such as Volkswagen and German chemical group BASF continue to increase their investments in China.
Russia, green energy industries
While bilateral economic relations will dominate the agenda of the trip, Zenglein and Zhang both said they think Scholz will still try to express German concern about China’s close partnership with Russia and their uneasiness about Chinese overcapacity in the green energy industries.
“Germany’s concern about China’s partnership with Russia will be a main element of the discussion because Scholz has a strong opinion about this,” Zhang told VOA. “But since Germany doesn’t have effective measures to pressure Beijing, Scholz’s warning won’t have much influence on how China evaluates its partnership with Russia.”
In Zenglein’s view, Scholz will try to “brush over” concerns about geopolitical risks quickly. “He will try not to get too hung up on the negative aspects of bilateral relations that might be counterproductive to positive developments in the bilateral economic relations,” he said.
…
Analysts: US military aid to allies would give US defense industry needed boost
As the Biden administration and the US Senate look to the US House to take up a bill for aid to Ukraine, Israel and Taiwan, experts say U.S. allies are not the only ones in need of the funding boost. As VOA Pentagon correspondent Carla Babb reports, some say the US defense industry desperately needs the boost as well.
Camera: Mary Cielak
…
How Russia’s disinformation campaign seeps into US views
Washington — On a near daily basis, Scott Cullinane talks with members of Congress about Russia’s war in Ukraine. As a lobbyist for the nonprofit Razom, part of his job is to convince them of Ukraine’s need for greater U.S. support to survive.
But as lawmakers debated a $95 billion package that includes about $60 billion in aid for Ukraine, Cullinane noticed an increase in narratives alleging Ukrainian corruption. What stood out is that these were the same talking points promoted by Russian disinformation.
So, when The Washington Post published an investigation into an extensive and coordinated Russian campaign to influence U.S. public opinion to deny Ukraine the aid, Cullinane says he was not surprised.
“This problem has been festering and growing for years,” he told VOA. “I believe that Russia’s best chance for victory is not on the battlefield, but through information operations targeted on Western capitals, including Washington.”
The Post investigation is based on more than 100 documents collected by a European intelligence service.
The files exposed a Kremlin-linked campaign in which “political strategists and trolls have written thousands of fabricated news articles, social media posts and comments that promote American isolationism, stir fear over the United States’ border security and attempt to amplify U.S. economic and racial tensions,” the Post reported.
Social media
One of the main methods for spreading such disinformation is social media, according to Roman Osadchuk, a researcher at the Atlantic Council’s Digital Forensic Research Lab and an expert on propaganda and influence campaigns.
“The process begins with a Russian publication on a small website or social media account. This is then picked up by a small Russian Telegram channel, which is subsequently shared by a larger channel with more subscribers,” Osadchuk said.
From there, someone will translate the content into English and share it, for example, on X.
“This is how Russian disinformation can quickly spread within the English-speaking X community,” Osadchuk said.
In an article published April 8, The Washington Post cited Microsoft and the social media intelligence company Graphika as saying that some articles created within this operation could have been first published on sites known as doppelgangers.
Osadchuk told VOA that these are deceptive replicas of legitimate media websites. They feature fake articles and are often taken down, only to be replaced by clones with slightly different web addresses.
“Nobody would know about these sites’ existence unless they are promoted on social media platforms. However, as soon as they detect them, social media block them. So, Russians quickly replace banned sites with their clones,” he said.
Worldwide effect
In interviews with U.S. media, two influential Republicans said they believe the propaganda has influenced their base and some of their colleagues.
“It is absolutely true. We see, directly coming from Russia, attempts to mask communications that are anti-Ukraine and pro-Russia messages, some of which we even hear being uttered on the House floor,” House Intelligence Committee Chair Mike Turner said in an interview with CNN.
In an interview with the U.S. news website Puck, Michael McCaul, head of the House Foreign Affairs Committee, said, “Russian propaganda has made its way into the U.S., unfortunately, and it’s infected a good chunk of my party’s base.”
Serhiy Kudelia, a political scientist at Baylor University, says the Kremlin messaging is effective because it plays on existing fears.
He says the disinformation seeks to reinforce already held beliefs such as the wastefulness of aid to Ukraine, or fuels existing anger and energizes opposition to sending assistance.
“When such alignment occurs, it is easier to push through disinformation and invented news stories that would be accepted as credible by a large number of people, including members of Congress, since they reinforce their prior beliefs,” Kudelia said.
“Once fabricated stories enter mainstream public debates, they become almost impossible to debunk or separate truth from lies,” he said.
The disinformation campaign is similar to ones seen in Europe. Both seek to decrease support for Ukraine, undermine public trust in their institutions and polarize society, says Jakub Kalenský, a senior analyst at Helsinki-based European Centre of Excellence for Countering Hybrid Threats.
Kalenský, who is deputy director of the center’s Hybrid Influence team, believes the Kremlin’s disinformation activities have a significant effect on politics worldwide.
“This is why Russia employs thousands of people for this activity. This is why they spend billions every year, because they see it works,” he said.
But Olga Belogolova, director of the Emerging Technologies Initiative at Johns Hopkins University, says that it is hard to know how effective these propaganda efforts are.
“Russian influence operations are not necessarily always designed to get people to believe anything in particular, but to get them to believe nothing at all,” she told VOA. Belogolova added that claims of the efforts being successful in swaying opinion “is not only irresponsible, it’s dangerous.”
Countermeasures needed
Last month, the U.S. Treasury Department issued sanctions on two people and two companies that it says are connected to a “foreign malign influence campaign.” They include Moscow-based Social Design Agency, its founder Ilya Gambashidze, Russia-based Group Structura LLC and its CEO Nikolai Tupikin.
The Social Design Agency and Gambashidze are believed to be involved in the campaign described in the Post article on April 8.
Kalenský advises governments on countering disinformation and says its success requires countermeasures.
These include strengthening detection and documentation of Russian disinformation campaigns, increasing awareness and resilience of audiences to the propaganda efforts, and preventing the aggressor from exploiting weaknesses of social media and societies.
“Finally, we need to impose higher costs on the information aggressors. So far, they are almost unopposed in conducting their aggression,” Kalenský said.
For Cullinane, the Russian disinformation campaign makes his job harder. He says the debate about the role the U.S. should play in the world appears to be shifting and invoking pre-World War II isolationism.
But he remains resolute. Part of his work is finding what resonates most with each lawmaker.
“Some offices focus very much on the human rights situation in Ukraine. Many members are very moved by the plight of religious communities in occupied territories of Ukraine and the persecution they face at the hands of the Russian military,” Cullinane said. “Other offices are very intrigued by the military reform and the military innovation brought about by an active war in Ukraine.”
The national security spending bill is currently awaiting approval in the House.
This story originated in VOA’s Ukraine Service.
…
Russia deceives foreigners to work, fight on Ukraine front lines, analysts say
In Telangana state, India, a man is desperately trying to get his brother back from the front lines in Ukraine after he was duped into working for Russia during its invasion of the country. Experts explain why Russia is using such subterfuge in its war effort. Henry Wilkins reports.
…
Wife of Julian Assange: Biden’s comments mean case could be moving in right direction
London — The wife of Julian Assange said Thursday her husband’s legal case “could be moving in the right direction” after President Joe Biden confirmed the U.S. may drop charges against the imprisoned WikiLeaks founder.
It came as supporters in several cities rallied to demand the release of Assange, on the fifth anniversary of his incarceration in London’s high-security Belmarsh prison.
Biden said Wednesday that his administration is “considering” a request from Australia to drop the decade-long U.S. push to prosecute Assange for publishing a trove of classified American documents. The proposal would see Assange, an Australian citizen, return home rather than be sent to the U.S. to face espionage charges.
Officials have not provided more details, but Stella Assange said the comments are “a good sign.”
“It looks like things could be moving in the right direction,” she told the BBC, saying the indictment was “a Trump legacy and really Joe Biden should have dropped it from day one.”
Assange has been indicted on 17 espionage charges and one charge of computer misuse over his website’s publication of classified U.S. documents almost 15 years ago. American prosecutors allege that Assange, 52, encouraged and helped U.S. Army intelligence analyst Chelsea Manning steal diplomatic cables and military files that WikiLeaks published, putting lives at risk.
Australia argues there is a disconnect between the U.S. treatment of Assange and Manning. Then-U.S. President Barack Obama commuted Manning’s 35-year sentence to seven years, which allowed her release in 2017.
Assange’s supporters say he is a journalist protected by the First Amendment who exposed U.S. military wrongdoing in Iraq and Afghanistan.
Assange has been in prison since 2019 as he fought extradition, having spent seven years before that holed up in Ecuador’s London embassy to avoid being sent to Sweden over allegations of rape and sexual assault.
The relationship between Assange and his hosts eventually soured, and he was evicted from the embassy in April 2019. British police immediately arrested and imprisoned him in Belmarsh for breaching bail in 2012.
The U.K. government signed an extradition order in 2022, but a British court ruled last month that Assange can’t be sent to the United States unless U.S. authorities guarantee he won’t get the death penalty.
A further court hearing in the case is scheduled for May 20.
Assange was too ill to attend his most recent hearings. Stella Assange has said her husband’s health continues to deteriorate in prison and she fears he’ll die behind bars.
…
Experts say Turkey becoming a drug transit hub
ISTANBUL — Turkish police have seized the third largest haul of cocaine in the country’s history, Interior Minister Ali Yerlikaya announced Thursday, as groups monitoring organized crime warned that the country was becoming an entry point for drugs reaching Europe.
Some 608 kilograms of cocaine, most of it in liquid form, were confiscated in an operation across three provinces, Yerlikaya posted on the social media platform X. Nearly 830 kilograms of precursor chemicals used to process the drug were also seized.
Yerlikaya said the police operation targeted an international gang allegedly led by a Lebanese-Venezuelan national, who was among four foreign members of the “organized crime group” detained, along with nine Turks.
“The amount of cocaine seized in the … operation was the third-largest amount of cocaine seized at one time in Turkey,” the minister added.
Groups monitoring organized crime say Turkey is growing as a transit hub for cocaine coming from South America to Europe as security at ports such as Rotterdam in the Netherlands becomes tighter.
In a report dated October last year, the Global Initiative Against Transnational Organized Crime said a 44% rise in cocaine seizures in Turkey between 2021 and 2022 was not reflected in data on domestic consumption, “suggesting that the country is likely to serve as a drug corridor.”
Officials made Turkey’s largest seizure — 1.1 tons of cocaine hidden in a consignment of bananas from Ecuador — at the Mediterranean port of Mersin in 2021.
Since coming to office in June last year, Yerlikaya has overseen a clampdown on organized crime in Turkey to counter claims the country has become a haven for foreign gangsters.
He regularly posts details of the latest police operation to target drug traffickers, fraudsters and other criminals.
Thursday’s social media post included a video, overlaid with dramatic music, showing apparent surveillance footage, large plastic containers and a pressing machine.
The operation was led by anti-narcotics officers based in Kocaeli, which lies southeast of Istanbul, but also included investigations in Tekirdag to Istanbul’s northwest and in the Mediterranean province of Antalya.
The gang used vineyards in Tekirdag and Antalya to store chemicals and process the cocaine, which had been disguised in fertilizer, according to Yerlikaya. A shotgun was also recovered by police, he added.
“We will not tolerate poison traffickers, organized crime groups and gangs, whether national or international,” the minister wrote.
…
Nine people killed as boat capsizes in Mediterranean, Italy coast guard says
Rome — Nine people, including a baby, have died after their boat capsized while trying to cross the Mediterranean in stormy weather, and another 15 people are feared missing, Italy’s coast guard said on Thursday.
The Italian coast guard said it received a cooperation request from the Maltese search and rescue (SAR) authority after the boat capsized approximately 50 kilometers southeast of the island of Lampedusa on Wednesday.
The coast guard said it dispatched its own patrol boat to the scene, which “rescued 22 survivors and recovered 9 deceased individuals, including a baby.”
The rescue operations “were particularly challenging due to adverse weather and sea conditions in the area with waves up to 2.50 meters,” the coast guard said.
The nationality of the boat’s passengers was not known but Lampedusa, which sits in the Mediterranean between Tunisia, Malta and the larger Italian island of Sicily, is the first port of call for many migrants seeking to reach the European Union.
“New terrible shipwreck near Lampedusa during a rescue operation,” UNHCR Communication Officer Filippo Ungaro posted on X late on Wednesday. The survivors, taken to Lampedusa, were “in a state of hypothermia and shock,” he added.
An aircraft from the Italian coast guard was conducting aerial searches for the missing in the area of the shipwreck.
In a separate operation, the Italian coast guard said it rescued 37 migrants “who were at the mercy of the waves aboard a small wooden boat about 7 meters long” off the coast of Lampedusa on Wednesday.
…
Top US general warns Ukraine on brink of being overrun by Russia
WASHINGTON — The tenacity of Ukrainian troops will soon be no match for Russia’s manpower and missiles should U.S. lawmakers fail to approve additional security assistance for Ukraine, the top American general in Europe told lawmakers, part of a stark warning about the direction of the more than two-year-old conflict.
U.S. military officials have warned repeatedly in recent weeks that Russian forces have been able to make incremental gains in Ukraine and that without renewed U.S. backing, Ukraine’s forces will eventually falter.
Testifying before the House Armed Services Committee Wednesday, the commander of U.S. European Command described the battlefield in blunt terms.
“If we do not continue to support Ukraine, Ukraine will run out of artillery shells and will run out of air defense interceptors in fairly short order,” said General Christopher Cavoli, explaining that Kyiv is dependent on the United States for those key munitions.
“I can’t predict the future, but I can do simple math,” he said. “Based on my experience in 37-plus years in the U.S. military, if one side can shoot and the other side can’t shoot back, the side that can’t shoot back loses.”
Cavoli also said the failure of U.S. lawmakers to approve a $60 billion supplemental security package is already giving Russia a significant advantage.
“They [Ukraine] are now being outshot by the Russian side 5-to-1,” he told lawmakers. “That will immediately go to 10-to-1 in a matter of weeks.
“We are not talking about months. We are not talking hypothetically,” Cavoli said.
Multiple U.S. officials have warned that Ukraine’s military has been forced to ration artillery and air defense capabilities as Kyiv waits for U.S. lawmakers to approve the supplemental assistance.
“We are already seeing the effects of the failure to pass the supplemental,” Assistant Secretary of Defense Celeste Wallander told the panel, testifying alongside U.S. European Command’s Cavoli.
“We don’t need to imagine,” she said, blaming the lack of U.S. provided artillery for why “the Russian attacks are getting through.”
That supplemental defense package passed in the U.S. Senate back in February, but leadership in the House of Representatives has so far refused to bring the legislation to the floor for a vote.
During a press conference on Capitol Hill Wednesday, Republican House of Representatives Speaker Mike Johnson said lawmakers were continuing to “actively discuss our options on a path forward.”
“It’s a very complicated matter at a very complicated time. The clock is ticking on it, and everyone here feels the urgency of that,” Johnson said. “But what’s required is that you reach consensus on it, and that’s what we’re working on.”
House Democrats, however, have voiced frustration with Johnson’s refusal to call a vote.
“The House has waited months now to approve the security package to help protect Ukraine,” said Representative Adam Smith, the top Democrat on the House Armed Services Committee. “Weeks ago, we were too late. And now every day is at an extreme cost to our ability to deter Russia.”
Another Democrat on the committee, Representative Elissa Slotkin, scolded Johnson, saying he needs to call a vote despite opposition from a small group of House Republicans.
“We do need to get it over the finish line,” she said. “I accept that he’s at risk of losing his job over that choice, but that’s what leadership is — it’s the big boy pants and making tough choices.”
Some Republicans, though, chastised Democratic lawmakers for what they described as misguided priorities.
“We’ve got hundreds of thousands of Americans who are dying, fentanyl overdoses, child and human sex trafficking, not to mention 178-plus countries that are crossing our border,” said Republican Representative Cory Mills.
“But, oh wait, that’s not the priority. Let’s secure Ukraine’s borders,” he said.
VOA’s Katherine Gypson contributed to this report.
…
EU lawmakers approve an overhaul of migration law, hoping to deprive the far right of votes
BRUSSELS — European Union lawmakers approved Wednesday a major revamp of the bloc’s migration laws aimed at ending years of division over how to manage the entry of thousands of people without authorization and depriving the far right of a vote-winning campaign issue ahead of June elections.
The members of the European Parliament voted on the so-called Pact on Migration and Asylum, regulations and policies meant to help address the thorny issue of who should take responsibility for migrants when they arrive and whether other EU countries should be obliged to help.
The proceedings were briefly interrupted by a small but noisy group of demonstrators in the public gallery who wore shirts marked “this pact kills” and shouted “vote no!”
The 27 EU member countries must now endorse the reform package, possibly in a vote in late April, before it can enter force.
The plan was drawn up after 1.3 million people, mostly those fleeing war in Syria and Iraq, sought refuge in Europe in 2015. The EU’s asylum system collapsed, reception centers were overwhelmed in Greece and Italy, and countries further north built barriers to stop people entering.
But few have admitted to being happy with the new policy response to one of Europe’s biggest political crises, and even the lawmakers who drafted parts of the new regulations are unwilling to support the entire reform package.
“I’m not going to open a bottle of champagne after this,” Dutch lawmaker Sophie i’nt Veld, who drew up the assembly’s position on migrant reception conditions, told reporters on the eve of the plenary session in Brussels. She said she planned to abstain from some of the votes.
In’t Veld described the pact as “the bare minimum” in terms of a policy response, but she does not want to torpedo it by voting against. “We will not have another opportunity to come to an agreement,” she said.
Swedish parliamentarian Malin Bjork, who worked on refugee resettlement, said that the pact does not respond to “any of the questions it was set to solve.”
She said the reform package “undermines the individual right to seek asylum” in Europe because it would build on plans that some EU countries already have to process migrants abroad. Italy has concluded one such deal with Albania.
“We cannot have a situation where people systematically, in their thousands, die on their way seeking protection and refuge in Europe,” Bjork told reporters.
The new rules include controversial measures: facial images and fingerprints could be taken from children from the age of 6, and people may be detained during screening. Fast-track deportation could be used on those not permitted to stay.
“The pact will lead to more detention and de facto detention at the EU’s external borders, including for families with children, which is in clear violation of international law,” said Marta Gionco from Picum, a network of migrant rights defense organizations.
Mainstream political parties want to secure agreement on the pact ahead of Europe-wide elections on June 6-9. Migration is likely to be a campaign issue, and they believe the new reforms address concerns about an issue that has been a consistent vote-winner for far-right parties.
…
US restricts trade with companies tied to drones used by Russia, Houthis
WASHINGTON — The United States restricted trade with five companies on Wednesday that it said help produce and procure drones for use by Russia in Ukraine and by Iran-backed Houthis in Red Sea shipping attacks.
The companies from Russia and China were among 11 additions to the Commerce Department’s Entity List, which means suppliers need licenses before shipping goods and technology to them.
Russia has intensified its drone and missile strikes against Ukrainian energy facilities in recent weeks, causing significant damage and threatening a repeat of the blackouts experienced in the first year after Russia invaded Ukraine in February 2022.
The Commerce Department added a Chinese entity, Jiangxi Xintuo Enterprise Company, for supporting Russia’s military through the procurement, development and proliferation of Russian drones, it said.
Shenzhen Jiasibo Technology Company of China was cited for being part of a network procuring aerospace components, including drone applications, for an aircraft company in Iran. Three Russian entities — Aerosila JSC SPE, Delta-Aero LLC, and JSC ODK-Star — were added for being part of the network.
“These components are used to develop and produce Shahed-series UAVs which have been used by Iran to attack oil tankers in the Middle East and by Russia in Ukraine,” the Federal Register notice said, referring to unmanned aerial vehicles.
Attacks on ships, including oil tankers, by Iranian-backed Houthis have disrupted global shipping through the Red Sea. Yemen’s Houthi militia say they are retaliating against Israel’s war against Palestinian Hamas militants in Gaza.
Companies are added to the U.S. Entity List when Washington deems them a threat to U.S. national security or foreign policy. Suppliers must then be granted licenses, which are likely to be denied, before shipping goods to entities on the list.
The two United Arab Emirates citations, Khalaj Trading LLC and Mahdi Khalaj Amirhosseini, were added for apparently violating Iran sanctions by exporting or trying to export items from the United States to Iran through UAE, according to the posting.
Four Chinese entities were cited for acquiring U.S. items to support China’s military modernization efforts, it said. They are LINKZOL (Beijing) Technology Company, Xi’an Like Innovative Information Technology Company, Beijing Anwise Technology Company and Sitonholy (Tianjin) Company.
U.S.-Chinese military contacts resumed late last year, but tensions continue due to fundamental differences over Taiwan and the South China Sea that remain dangerous potential flashpoints.
Chinese leader Xi Jinping has pumped billions into buying and developing equipment as part of his modernizing efforts to build a “world-class” military by 2050, with Beijing’s outsized defense budget growing at a faster pace than the economy for some years.
…